This doc explains how our on-host integrations collect and report data.
Data collection and reporting process
This is how on-host integrations send data to New Relic:
- On startup, the infrastructure agent scans the directory that contains the integration's definition files.
- The infrastructure agent registers every integration executable defined in the definition file.
- The agent scans a dedicated directory for integration configuration files.
- If those config files specify integrations that have been registered with the infrastructure agent, the agent sets up and schedules the integrations.
- At the scheduled interval (the default is 15 seconds), the agent harvests the data from the integration and prepares it for transmission. Every 60 seconds, it sends that data to New Relic, along with any other infrastructure data.
- After a successful collection pass, the integration executable exits.
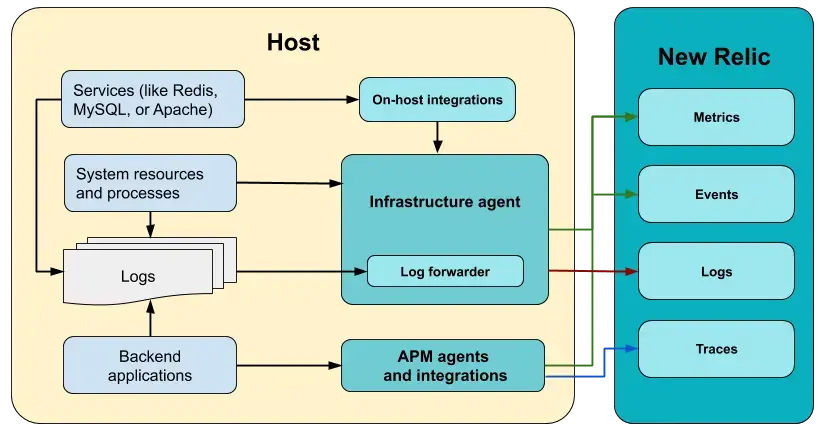
Integration architecture
Here's an example of how the SQL Server integration works:
- Host 1 with the infrastructure agent installed needs an outbound rule for port
1433. - Host 2 with SQL Server needs an inbound rule for port
1433.
In this example, host 1 pulls data from host 2.
File structure and specifications
Understanding the file structure of these on-host integrations can help you customize your integration, understand and use your data, and troubleshoot problems.
These integrations adhere to a set of open source specifications. For an explanation of these file specifications, see File specs.