The Kubernetes APM auto-attach, formerly known as the Kubernetes agent operator, streamlines full-stack observability for Kubernetes environments by automating APM instrumentation alongside Kubernetes agent deployment. By enabling auto instrumentation, developers no longer need to manually manage APM agents. The Kubernetes APM auto-attach will automatically install, upgrade and remove APM agents.
It currently supports Java, .NET, Node.js, Python, Ruby, and PHP.
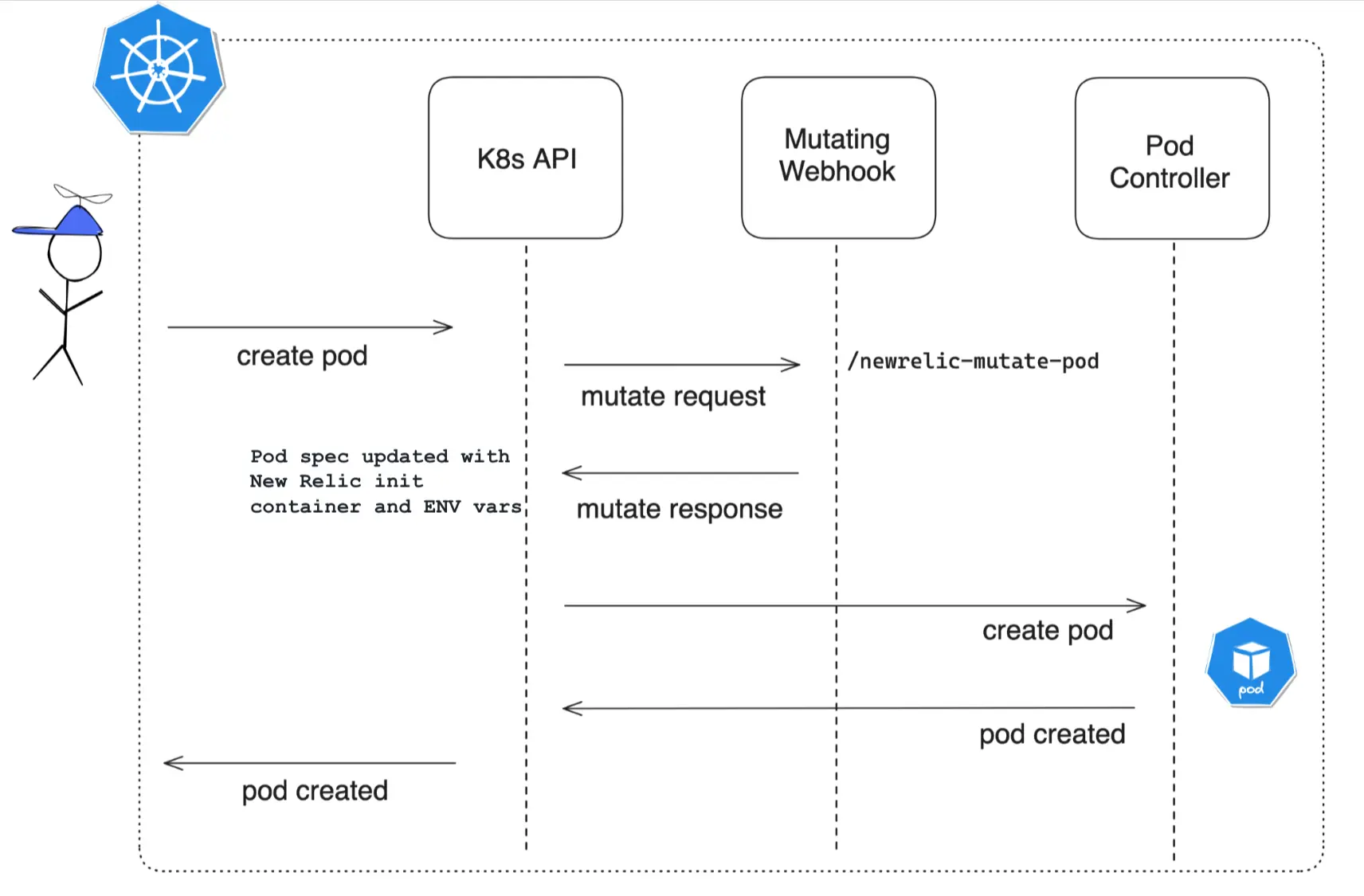
How it works
The
MutatingWebHook, upon installation, becomes involved in intercepting API requests for deploying pods onto nodes.Reflecting the configurations specified, it mutates the pod specification to add a NR init container and environment variables.
Following the establishment of the pod, the New Relic APM Agent is seamlessly integrated into the application housed within it.
Before you begin
Before installing the operator, check the following:
Helm: You must install it to use the charts. See the Helm documentation if you need help getting started.
Kubectl: You have to configure it to communicate with your cluster.
Installation
Depending on what you need, you can choose to install the Kubernetes APM auto-attach independently or together with our Kubernetes integrations.
We strongly recommend to install it together with the Kubernetes integration to take advantage of our entire full stack observability experience.
Bundle installation in addition to the Kubernetes integration (recommended)
The Kubernetes APM auto-attach chart is part of the nri-bundle chart, which manages the installation of all the components needed to enable a full Kubernetes observability.
Add the k8s-agents-operator.enabled=true parameter to your helm command or include it in the values.yaml file. See the Install the Kubernetes integration page for more information about using Helm or check out the nri-bundle chart.
See this sample of Helm commands using parameters:
$helm repo add newrelic https://helm-charts.newrelic.com$
$helm upgrade --install newrelic-bundle newrelic/nri-bundle \> --set global.licenseKey=YOUR_NEW_RELIC_INGEST_LICENSE_KEY \> --set global.cluster=CLUSTER_NAME \> --namespace=newrelic \> --set newrelic-infrastructure.privileged=true \> --set global.lowDataMode=true \> --set kube-state-metrics.enabled=true \> --set kubeEvents.enabled=true \> --set k8s-agents-operator.enabled=true \> --create-namespaceStandalone installation
To install the Kubernetes APM auto-attach with the default configuration, run these commands:
$helm repo add k8s-agents-operator https://newrelic.github.io/k8s-agents-operator$helm upgrade --install k8s-agents-operator k8s-agents-operator/k8s-agents-operator \> --namespace newrelic \> --create-namespace \> --set licenseKey=YOUR_NEW_RELIC_INGEST_LICENSE_KEYFor a complete list of configuration options, see the README chart.
Configure auto-instrumentation
After APM auto-attach is all set up in your cluster, the next step is just to roll out the configs required to get it operational. That involves having at least one instrumentation Custom Resource (CR) active in the cluster.
Here's what the instrumentation CR lets you map out:
- Name of the instrumentation CR
- Where it will apply the instrumentation CR using
selectors - APM agent (one per CR)
- APM agent version
- APM config parameters (env vars)
- License key (optional)
The manifest file needs to injected in the same namespace (newrelic by default) where you installed APM auto-attach.
$kubectl apply -f ./instrumentation.yaml -n newrelicHere you have a complete instrumentation.yaml for your reference.
How to use selectors
Use selectors to control which resources the CR injects with APM agents. Three selectors are available. You can use them individually or in combination. When combined, the selectors are evaluated using a logical AND (&&) operation.
MatchLabel and MatchExpressions
All the selectors support matchLabel and matchExpressions.
APM agent
You've got to specify the APM agent and its version within the instrumentation CR. We recommend using the latest version to take advantage of the newest features available.
Language | Image | Available versions |
|---|---|---|
dotnet |
| |
dotnet-windows2022 |
| |
dotnet-windows2025 |
| |
java |
| |
nodejs |
| |
python |
| |
ruby |
| |
php |
|
See this example:
...spec: agent: language: dotnet image: newrelic/newrelic-dotnet-init:latest...APM configuration
Using environment variables
The instrumentation CR provides the capability to inject environment variables in the pod to streamline the configuration of the APM agents. See this example:
...spec: agent: env: # Example overriding the appName configuration by using a label of the pod - name: NEW_RELIC_APP_NAME valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.labels['app.kubernetes.io/name']...In the above example, we show you how you can configure the agent settings globally using environment variables. See each agent's configuration documentation for available configuration options:
중요
You can inject these environment variables in the app deployment manifest.
Using a configmap (Java only)
When using the configmap, note the following requirements:
- The Java configuration must be stored in a key named
newrelic.yaml. - Setting the application name or license key in the
configmapis not supported. - To set these properties, use environment variables or custom secrets instead.
apiVersion: newrelic.com/v1beta2kind: Instrumentationmetadata: name: newrelic-instrumentation-java namespace: newrelicspec: agentConfigMap: "my-java-app-config" # This configmap must exist in every namespace that the pod in this `Instrumentation` is targeting agent: ...License keys (optional)
When you install it, a is created and it's the license by default. Follow these steps, if you need to send the APM telemetry to a different account:
To create a secret containing a new license key, run this command:
bash$kubectl create secret generic newrelic-key-secret \>--namespace my-monitored-namespace \>--from-literal=new_relic_license_key=YOUR_NEW_RELIC_INGEST_LICENSE_KEYTo reference the secret from the instrumentation CR, run this command:
...spec:licenseKeySecret: the-name-of-the-custom-secret...
Instrumentation CR examples
Update APM instrumentation in applications
By default, the Kubernetes APM auto-attach automatically installs the latest available version of the corresponding APM agent.
Once the monitoring of an application starts, it's not automatically updated to a newer version unless you choose to update. You can update the application by redeploying the pods or restarting your deployment.
Remove APM instrumentation in applications
To remove the APM instrumentation from an application, you must change the matching label selector inside either the podLabelSelector or namespaceLabelSelector used or delete the instrumentation CR. Then, restart the deployment. The remove process takes just a few seconds.
Update the Kubernetes APM auto-attach
Bundle installation
Run an update of the nri-bundle chart with the following parameter:
$k8s-agents-operator.enabled=trueStandalone installation
Run the helm upgrade command to update to a newer version of the Kubernetes APM auto-attach.
$helm upgrade k8s-agents-operator newrelic/k8s-agents-operator -n newrelicUninstalling the Kubernetes APM auto-attach
Bundle installation
Uninstall the nri-bundle chart or if you only want to remove Kubernetes APM auto-attach, run a helm upgrade with the following parameter:
$k8s-agents-operator.enabled=falseStandalone installation
To uninstall and delete the Kubernetes APM auto-attach, run this command:
$helm uninstall k8s-agents-operator -n newrelicFind and use data
Get insights of your applications and resolve alert events using the APM summary page.
Check out the Kubernetes summary page. It provides Kubernetes insights in the context of your monitored applications.
Certificates
The Kubernetes APM auto-attach can support cert-manager if preferred.
Run this command to install the
cert-managerHelm chart:bash$helm install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \>--namespace cert-manager \>--create-namespace \>--set crds.enabled=trueIn your
values.yamlfile, setadmissionWebhooks.autoGenerateCert.enabled: falseandadmissionWebhooks.certManager.enabled: true. Then, install the chart as normal.
Available chart releases
Run this command to see the available charts:
$helm search repo k8s-agents-operatorFrequently asked questions
Troubleshooting
If your applications are not instrumented, you should check the following:
Please be sure to redeploy or deploy new applications after you've installed Kubernetes APM auto-attach. Notice that only auto-instruments new applications are deployed in the cluster.
Run this command to check that the secret is installed in the app's namespace:
bash$kubectl get secrets -n NAMESPACECheck that the pod has the required labels that enable automatic instrumentation through CR when using
podLabelSelector. Similarly, check that the namespace has the required labels when usingnamespaceLabelSelectorinside the CR.bash$kubectl get pod POD_NAME -n NAMESPACE -o jsonpath='{.metadata.annotations}'Run this command to get logs from the APM auto-attach pod:
bash$kubectl logs AGENT_OPERATOR_POD -n newrelicRun this command to ensure the
initcontainer has been injected and sucessfully executed inside the application's pod.bash$kubectl describe pod POD_NAME -n NAMESPACE
How to migrate from previous versions that required annotations
Starting with version 0.14, annotations within the application deployment manifest are no longer necessary for applications to be auto-instrumented.
It's advised to uninstall any versions preceding 0.14 and proceed with the installation of the latest release. Utilizing the label selectors within the instrumentation CR will enable the precise deployment of APM agents, thereby obviating the requirement for annotations.
Support
Kubernetes APM auto-attach supports the following languages and their minimum supported versions according to our standard APM agent support policy:
- Java Agent: 8.12
- .NET Agent: 10.25
- Ruby Agent: 9.10
- Node.js Agent: 11.9
- Python: 9.10
- PHP: 11.12
For any issues:
Review the issues section on GitHub for any similar problems or consider opening a new issue.
You can reach out to the New Relic support team for assistance.